Search engines like Google rely on more than 200 ranking factors for search engine optimization (SEO). With the rapid pace of algorithm updates, it’s a challenge to stay ahead of the latest and most critical SEO factors. Fortunately, you have this comprehensive list of SEO ranking factors*.
Keep reading to learn more about the search engine ranking factors used by companies like Google and Bing. Plus, gain insight into the most important SEO factors for this year so that you can build a competitive, white-hat strategy that puts your site on the first page!
P.S. For everyone who wants more traffic from their site, there is SEO Checker. Enter your URL to get a complete SEO audit, plus personalized recommendations for improving your SEO so your website can capture more traffic!
*Most search engines do not provide an exact breakdown of their ranking factors or the weight of those factors to prevent spammers from manipulating search results. This list of SEO ranking factors includes confirmed factors, as well as some believed (via studies) to influence rankings in search results.
Table of Contents
- 5 most important SEO ranking factors
- SEO starter resources: Go beyond ranking factors
- Domain
- Site
- Page
- Content
- Multimedia
- Keywords
- Anchor Text
- Inbound Links
- User
- Google Algorithm
- Social
The 5 Most Important SEO Factors You Can’t Afford to Ignore
With over 200 search engine ranking factors, reviewing each one can be time-consuming. By focusing on the factors that most influence your search result positions, you can start auditing your site, re-optimizing your content, and climbing the search results more efficiently. That's why we've highlighted the five most critical SEO factors for you:
1. Responsive Design
A responsive design that adapts to any device is crucial for ranking in results. Since search engines like Google use a mobile-first index, their crawlers view your site from a mobile perspective. If your website isn’t mobile-friendly, it will struggle with usability and accessibility ranking factors. Use Google's Mobile-Friendly tool to check your website’s mobile experience.
That’s because search engines like Google use a mobile-first index, which means its crawlers view your site from the perspective of a mobile user, versus desktop user. If your website isn’t mobile-friendly, then it’s going to fail when it comes to search ranking factors related to usability and accessibility
2. Page Speed
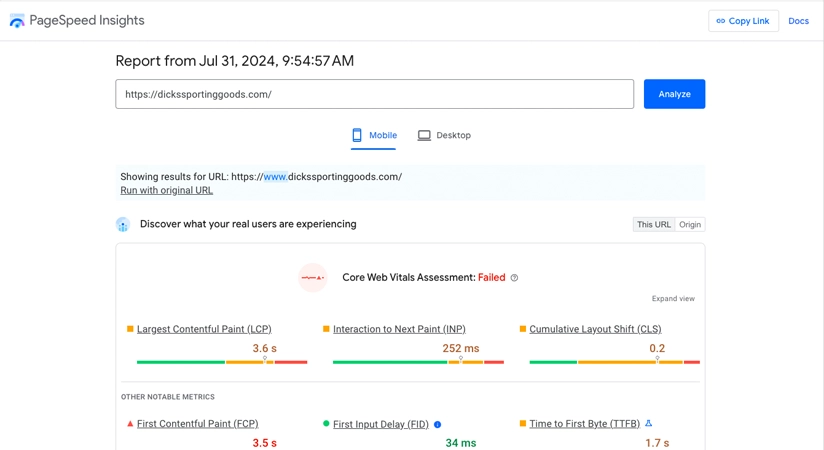
Page speed is a vital SEO ranking factor, and Google acknowledges its importance. Besides viewing your site from a mobile perspective, Google also checks your site’s speed. If your site is slow, it can affect your rankings.
Test your speed with Google's PageSpeed Insights tool and consider page speed optimization services if you need help implementing fixes.
3. Links
Links, including backlinks and internal links, are critical for search engine rankings. Backlinks from trusted and authoritative sites signal to Google that your site provides valuable content.
Creating top-notch content and conducting outreach can help attract backlinks. Internal links help search engine crawlers explore and index your site, understand relationships between pages, and provide context. A robust link-building strategy and internal linking process are essential for top rankings.
4. On-Page Optimization
On-page optimization involves several SEO ranking factors such as:
- Keyword usage
- Title tag optimization
- Content originality and usefulness
- Multimedia optimization
- And more
Incorporate keywords throughout your content, headers, and title tags, and optimize images for context and size. Missing any step, like not optimizing your title tag, can result in missed ranking opportunities.
5. Accessible Website
For search engines to rank your site, they need to crawl and index it. Ensure your website is accessible with a robots.txt file and sitemap. Submit your site, pages, and sitemap to Google via Google Search Console. An intuitive and easy-to-use site for users is equally important. If users struggle to navigate your site, maintaining your rankings will be challenging.
[CALLOUT]Go beyond SEO ranking factors: Helpful resources for the SEO beginner
Before diving into the ranking factors that search engines like Google use, you might want to check out these helpful resources for SEO beginners.
These articles and guides can answer your questions and get you up to speed on the latest in search engine optimization.
- SEO: Complete Optimization Guide
- Google SEO: The Complete Google Optimization Guide
- The Definitive SEO Checklist
- Ongoing SEO Best Practices for Beginners and Pros
- How to Learn SEO for Free (At Home!)
- What Does SEO Stand For?
- How Does SEO Work?
- How to Know If Your SEO Is Working
- SEO Help for Beginners: How to Improve Your SEO Like a Pro
Once you've reviewed (or bookmarked) these articles, continue reading to learn all about search ranking factors!
SEO Ranking Factors: Domain
The strength of your domain is a significant factor in SEO. Essentially, your domain is taken into account when users enter search queries related to your website. The more credibility you’ve built through both on-page and off-page factors, the more favorably Google will view your domain.
1. Domain Age
Google states that domain age doesn’t significantly impact ranking. A Google Webmasters YouTube video mentions, "The difference between a domain that’s six months old versus one-year-old is really not that big at all.”
2. Domain Registration Length
Domains registered for over a year tend to appear more credible, having outlived the typical lifespan of doorway domains. A Google patent supports this as a ranking factor, but some Google team members disagree, noting that most registrars don’t consider registration length. It's not worth focusing your SEO efforts here.
3. Domain History
Domains with gaps in registration or dubious histories may struggle with ranking. This can be problematic when purchasing a domain previously used for spam or black-hat activities. Always check a domain's history on archive.org before purchasing.
4. Domain Authority of Page Host
New pages on authoritative domains generally rank better than those on lesser-known domains. While domain authority itself isn’t a ranking factor, it predicts the likelihood of one domain outranking another. That's why SEOs reference it.
5. Parked Domains
Google can identify parked domains and generally ranks them poorly due to their poor user experience. In 2011, Google stated that it prefers not to show parked domains because they offer little value to users.
6. Exact Match Domain (EMD)
Having a quality website with an exact match domain (EMD) like "hikingshoes.com” can boost your search rankings. However, in 2012, Google started penalizing low-quality or spammy EMDs, such as "buynewshoes.com.” While an EMD can offer some advantages, it's crucial to ensure your site delivers valuable content to users.

7. Country-Specific TLD or Extensions
A country code (e.g., .tv, .cn, .de) may help your site rank in that country by signaling relevance to users there. However, it may limit your ability to rank globally.
8. Server Flagged as Spam
If you share a server with spammy sites, it can affect your ranking. Google understands shared hosting, but if a server has a high percentage of spammy sites, Google may scrutinize your site more closely.
9. Domain Flagged as Spam
If your domain is flagged for spam, it can negatively impact your site’s performance. Even if penalties are remedied, Google remains cautious due to spammers potentially using tactics to make a domain appear trustworthy again.
10. Concise URLs
Simple and descriptive URLs help Google understand your page content. Although a minor ranking factor, concise URLs assist both crawlers and users, enhancing your SEO.
11. URL String
Easy-to-read URLs send positive signals to Google. Shorter URLs generally perform better in search results. Aim for URLs with 50 to 60 characters for the best results.
12. Public vs. Private WhoIs
Public WhoIs information can keep your site in good standing. Although private WhoIs isn’t inherently bad, it can raise concerns if combined with other negative factors.
13. Spammy WhoIs Owner
If the owner of a domain has a history of spammy practices, Google may consider this when ranking sites owned by that individual.
14. Server Locations
The physical location of your servers can impact rankings in location-specific queries. Google aims to return the most relevant results for users in each country, and server location (in terms of IP address) is a factor.
SEO Ranking Factors: Site
Site SEO ranking factors encompass elements that affect your entire website. These include categories like infrastructure, stability, reliability, and more. To maintain a strong position in SERPs, ensure your site operates smoothly for both search engines and users.
15. SSL / HTTPS

A Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate provides your URL with the HTTPS designation, indicating a secure site. While Google uses HTTPS as a "very lightweight signal,” it significantly builds user trust.
16. Site Architecture
A well-coded, clean site architecture is easy for Google to crawl and index. Google recommends that all pages should be accessible via links on your site, not just through a sitemap, to maintain context.
17. Site Usability
Websites with smooth, intuitive interfaces rank better than those that are difficult to navigate. Poor usability leads to high bounce rates, negatively impacting rankings.
18. Site Reliability or Uptime
Frequent crashes or downtime can hurt your rankings. While short-term outages (a few hours or a day) typically don't affect rankings, extended downtimes (weeks) can.
19. Site Reputation or Reviews
Positive reviews on sites like Yelp can enhance your rankings. Negative reviews can harm visibility, though Google has mechanisms to mitigate extreme cases of negative review manipulation.
20. Site Over-Optimization
Over-optimization can lead to penalties. Google confirms that optimizing excessively can harm your rankings, as it might be viewed as manipulative.
21. Frequency of Site Updates
Regularly publishing fresh, unique content is favored by Google. While frequency alone doesn’t guarantee higher visibility, it helps in creating content that attracts and engages your target audience.
22. Duplicate Meta Descriptions Across Site
Duplicate meta descriptions make it harder for Google to crawl and understand your pages. While not usually penalized, duplicate content can signal a lack of unique value.
23. Spammy Meta Descriptions
Misleading or spammy meta descriptions can lead to penalties. Provide original, accurate summaries of your pages to encourage clicks.
24. Mobile-Friendly or Responsive Site Design
Mobile-friendliness is a ranking factor. Sites that aren’t mobile-friendly can suffer in SERPs. Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool to ensure your site meets this criterion.
25. Breadcrumb Navigation

Breadcrumb navigation helps users and Google navigate your site easily. Follow Google’s guidelines for implementing breadcrumb navigation.
26. HTML Sitemap
An HTML sitemap aids Google in crawling and indexing your site thoroughly. While it doesn’t directly affect rankings, it can improve site visibility.
27. Site-Wide Content Changes
Major changes, like a redesign, can signal a freshness factor to Google. However, if changes negatively impact site speed or usability, rankings can drop.
28. "Contact Us" Pages
A well-detailed "Contact Us” page can boost local SEO by listing your name, address, and phone number. Google’s guidelines highlight the importance of having contact information.
29. Time on Site
When a visitor stays on your page for a few minutes, it boosts the page's credibility more than a quick exit. Longer visits indicate that your website and content are effectively meeting the visitor's needs and interests.
30. Hacked Site
A hacked site can severely harm visibility and may even be deindexed by Google (as demonstrated by the case study of Search Engine Land). Use Google’s Help for Hacked Sites” if you suspect a breach.
Ensure your site aligns with these SEO ranking factors to maintain and improve your search engine visibility.
SEO Ranking Factors: Page
Everything you add to a page can influence Google’s perception of it. Adhering to their recommended guidelines makes it easier for their bots to crawl your pages and find the necessary information.
The more thorough you are with your page construction, the more likely it is to rank well.
31. Microformat or Structured Data Support
Pages with microformat or structured data may rank better.
According to Google, "There’s no generic ranking boost for [structured data] usage…However, [structured data] can make it easier to understand what the page is about, which can make it easier to show where it’s relevant.”
32. Page Loading Speed
Faster page loading speeds improve rankings in both mobile and desktop search results. Google uses page speed as an SEO ranking factor because it significantly impacts user experience. Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool to check your site’s speed.
33. Page Speed in Chrome
Google uses data from Chrome users to deliver PageSpeed Insights scores, providing direct insight into how most users experience your site and its speed.
34. Code and W3C Compliance
Efficient coding and adherence to W3C guidelines help with SEO. While Google doesn’t boost rankings for well-coded pages, it may penalize poorly coded, excessively large pages.
35. Doorway Pages
Doorway pages negatively affect rankings. These pages funnel users to the same destination, which Google penalizes because they provide a poor user experience.
36. Page Proximity to Homepage
Internal linking is crucial for SEO. Pages closer to the homepage may rank higher, especially in competitive search results.
37. PageRank
PageRank remains a core part of Google’s ranking factors. Higher PageRank generally correlates with more authoritative pages.
38. Page Age
Aged evergreen content can rank highly for relevant keywords. Keep evergreen pages updated to ensure they provide accurate and valuable information.
39. Page Categorization

Proper categorization of pages sends positive signals to Google. For example, organizing pages under relevant categories like "https://www.example.com/products/shoes” helps with ranking.
40. Page Sources
Citing quality references can enhance your trustworthiness. Although Google denies that outgoing links are a ranking factor, studies suggest that relevant outgoing links to trusted sites influence rankings.
41. Page Layout
An attractive, intuitive page layout that displays main content immediately, without intrusive ads, is crucial for rankings. Google’s 2012 update emphasized this factor, confirming its ongoing importance.
42. Tabs
Content hidden in tabs can impact SEO. While Google claims to crawl and index tabbed content, some studies suggest otherwise. Avoid tabs for a better mobile user experience.
43. Page Quantity
The number of pages on your site isn’t a ranking factor. However, additional pages can help target more keywords and demonstrate your site’s value. Ensure all content is original and useful.
44. Page Location in Sitemap
The placement of a page in your sitemap can indirectly influence ranking by helping Google crawl and index your site faster.
45. Rel=Canonical Tags

Canonical tags help manage duplicate content by indicating the preferred version of a page to Google, influencing other SEO ranking factors like syndicated content.
46. Popups and Distracting Ads
Using intrusive or flashy ads to divert users' attention away from the main content can negatively impact a website's ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). Google's "Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines" reinforce this SEO ranking factor. These guidelines advise against ads that are:
- Difficult-to-close
- Shocking
- Disturbing
- Require download of an app
47. Ads "Above the Fold”
Google penalizes sites with ads and thin content in the upper portions of their pages. Prioritize user experience to rank higher in search results.
48. WordPress Tags

Using tags on WordPress can help show the relationship between multiple posts. While some Google team members downplay their importance, they can aid in organizing content.
49. Page Over-Optimization
Over-optimizing pages with irrelevant or "toxic” assets can lead to penalties. Examples include keyword stuffing and multiple H1 headers on a single page.
50. Bounce Rate
For several years, Google team members have maintained that bounce rate isn’t the best SEO ranking factor due to its vulnerability to spamming. Despite this, SEOs continue to consider bounce rate important, as it often signals when a page fails to meet user expectations.
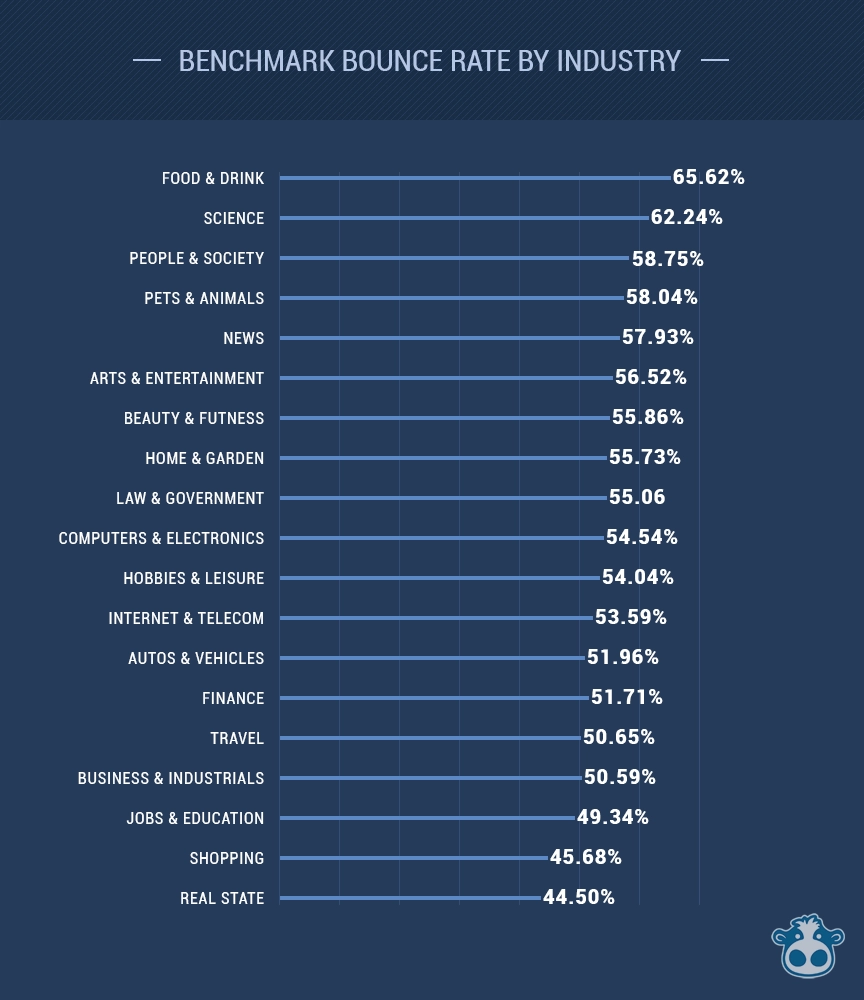
Although Google has debunked this notion, research suggests that bounce rate does influence SERPs. For instance, a 2017 SEMrush study of over 600,000 keywords found that bounce rate played a significant role in rankings.
51. DMCA
Google demotes pages with repeated DMCA complaints. Ensure your site doesn’t host copyrighted material without permission.
52. Direct Traffic
Sites with higher direct traffic are seen as higher quality by Google. Studies support direct website visits as a crucial ranking factor.
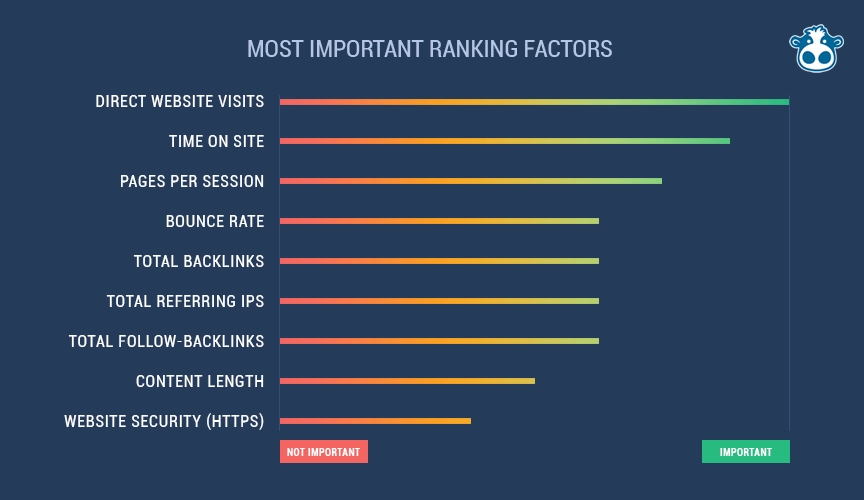
53. Repeat Traffic
Returning visitors can boost your rankings. Encourage repeat visits by publishing relevant and engaging content.
54. Terms of Service and Privacy Policy Pages
TrustRank measures trust signals, including Privacy Policy and Terms of Service pages. Creating these pages sends a positive signal to Google about your site’s trustworthiness.
By paying attention to these on-page SEO ranking factors, you can improve your site's visibility and performance in search results.
SEO Ranking Factors: Content
Content is crucial and serves as a valuable addition to any digital marketing strategy. These SEO ranking factors can be enjoyable to optimize, allowing bloggers, designers, and content creators to share their passions, discuss relevant news, and provide valuable content to real people. Creating content that offers a quality experience to users will make Google favor your site more.
55. Content Length
Longer content often reflects attention to detail and quality, attracting more social shares, organic traffic, and higher rankings. Studies show that longer content performs better in these areas.
56. Content Structure
Proper content structure, like including a table of contents, can improve performance in search results. SERPs may use these headings as sitelinks, boosting factors like click-through rate (CTR) and organic traffic.
57. Grammar and Spelling
While not a direct ranking factor, proper grammar and spelling correlate with higher page rank and reputation. Google's "Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines” frequently mention the importance of spelling, grammar, and punctuation.
58. Reading Level
Google recommends using clear and straightforward language, as users typically prefer regular words over technical jargon. Although not a major ranking factor, readability can influence user experience and engagement.
59. YMYL (Your Money, Your Life)
In recent updates, Google’s focused on improving “Your Money, Your Life” or YMYL results. Its “Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines” even mention that Google maintains, “very high Page Quality rating standards” for YMYL pages — specifically expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness or E-A-T. According to a recent white paper, Google says it tries to determine E-A-T via:
- PageRank
- Search Quality Evaluators
- Additional signals
For your content to succeed and rank for YMYL queries, you need to match E-A-T standards.
60. Co-occurrences
Co-occurrences involve the words around a backlink that help Google understand the content. For instance, if a blog post links to a recipe, terms like "baking” and "quick dessert” help Google identify it as a dessert recipe.
[pic]61. Relevant Terms or Semantic Search
Using a variety of related terms, rather than repeating the same keyword, can improve rankings. The Hummingbird and RankBrain updates emphasize the importance of semantic search.
62. Quality and Usefulness
Google favors sites with fantastic, interesting, and useful content. Combining quality with usefulness creates content that ranks well and provides value to users.
63. Insightful Content
Content that demonstrates thought and insight ranks well over time. Original and insightful content, including unique experiences, is the cornerstone of quality.
64. Unique Content
Unique content tells Google that your page is one-of-a-kind. Originality is a critical ranking factor because it matters significantly to users.
65. Holistic Content
A holistic approach covers topics comprehensively, addressing core subjects and related issues. For example, a guide on car maintenance might include what it involves, costs, and more.
66. Syndicated Content
Syndicated content should be modified enough to avoid being seen as duplicate content, which can cause ranking issues.
67. Automatically Generated Content
Autogenerated content often gets penalized by Google, especially if it's created to manipulate search results and users.
68. Additional Page Content
On-site interactives like calculators and planners provide additional value and context, helping Google assess relevance, usefulness, and quality.
69. Timeliness of Content
Google favors up-to-date content for time-sensitive or newsworthy queries. While not always favoring fresh content, Google prioritizes the latest information for certain searches.
70. Significance of Content Changes
Significant changes to trusted pages should retain as much valuable content as possible while adding more quality, in-depth text.
71. Frequency of Content Changes
Regular updates encourage Google to index your site more frequently, potentially increasing the number of pages in search results.
72. Google Panda and Content Quality
The Panda update penalizes low-quality content, emphasizing the importance of producing high-quality, useful, and original content.
73. Number of Comments
The number of comments on a blog or article can indicate its value and engagement, serving as a minor ranking factor.
SEO Ranking Factors: Multimedia
Multimedia elements like images, videos, and audio are essential for engaging users. Properly title, tag, and describe your multimedia content to make it accessible to search engine crawlers.
74. Multimedia
Multimedia content, including images, videos, and audio, engages users. Proper titling, tagging, and describing this content ensures search engine crawlers can read and understand it.
75. Image Alt Text
Descriptive and informative alt text helps Google understand the images on a page, aiding in featured snippets and top Google Images search results.
76. Image Optimization
Optimized images should have relevant alt text, file names, titles, descriptions, and captions, making them easier for Google’s crawlers to read and accessible to all users.
77. YouTube Optimization
YouTube videos often rank higher in SERPs than videos from other platforms. Optimize your YouTube account as it also serves as a strong SEO presence.
SEO Ranking Factors: Keywords
Using keywords strategically helps your site appear in SERPs related to your business. However, avoid over-optimization.
78. Keyword in Title Tag
Keyword-rich title tags are essential for ranking well. Keep them under 60 characters to avoid truncation by Google.
79. Keyword at the Beginning of Title Tag
Place keywords near the beginning of title tags while ensuring clarity and conciseness.
80. Keyword in URL
Keywords in URLs send relevancy signals to Google. While a minor factor, it’s beneficial to include targeted keywords in URLs.
81. Keyword as First Word in Domain Name
Keywords at the beginning of a domain name can be helpful but aren’t critical. Brandable domain names can also perform well.
82. Keyword in Domain
While less important than before, keywords in domain names can still send relevancy signals. Consider including keywords if it makes sense for your business.
83. Keyword in Meta Description Tag
[pic]Although not a ranking factor, including keywords in meta descriptions can send helpful relevancy signals to users and crawlers.
84. Keyword in H1 Tags
H1 tags serve as a secondary title tag, providing relevancy signals to Google and users. Multiple H1 headings on a page are acceptable.
85. Keyword in H2 and H3 Tags
Keywords in H2 and H3 tags signal relevancy, though not as strongly as H1 tags. Include core or related keywords in these headings.
86. Keyword Frequency
Using keywords more frequently than other phrases can signal relevancy. Avoid keyword stuffing, which can harm your rankings.
87. Keyword Density
Naturally interspersed keywords create a user-friendly appeal. Read your content aloud to spot excessive keyword density.
88. Keyword Prominence
[pic]Keywords in important locations like title tags, first paragraphs, and headings enhance keyword prominence.
89. Exact Keywords vs. Partial Keywords
Exact match keywords better reflect user intent, potentially ranking higher than partial matches.
90. LSI Keywords
Latent semantic indexing (LSI) keywords help contextualize your page, clarifying ambiguous terms.
91. LSI Keywords in Title and Description Tags
Using LSI keywords in title and meta description tags can help Google determine relevancy for topics with multiple contexts.
92. Quantity of Other Ranked Keywords on Site
Pages that rank well for multiple keywords signal quality, supporting new pages’ rankings.
93. Organic Keyword CTR
While not confirmed as a ranking factor, many SEOs believe organic CTR influences rankings due to mixed study results.
94. Organic CTR for All Keywords on Site
High organic CTR for all keywords on a site may indicate quality to Google, potentially influencing rankings.
95. Keyword in Subdomain
Keywords in subdomains can serve as a ranking factor, though not a primary concern for most webmasters.
Optimizing these factors can significantly improve your site’s visibility and performance in search results.
SEO Ranking Factors: Anchor Text
Anchor text refers to the text you use when linking to another site. The more descriptive and concise it is, the better the link appears to search engines. Additionally, Google’s crawler can infer context based on the surrounding words of anchor text, meaning the context around links also impacts your ranking.
96. Anchor Text Context
Google has a patent for reading link context, potentially sending significant relevancy signals to its crawlers.
97. Sentiment Around Anchor Text
The sentiment expressed around a link, whether positive or negative, can be gauged by Google and may impact your rankings.
98. Branded Anchor Text
Using a brand name in anchor text can send a strong signal to users and Google. However, avoid over-optimization. Some strategies involve finding mentions of your brand online and earning links for those mentions.
99. Spam Anchor Text
Identical anchor text, suspicious exact-match links, and other indicators of paid links can result in penalties. Google also flags text ads that pass PageRank, low-quality directory site links, and forum comments with optimized links as spam.
SEO Ranking Factors: Outbound Links
Google uses outbound links as an on-page ranking factor. Linking to credible sources, much like citing sources in an academic paper, can positively impact your rankings. However, excessive linking or linking to spammy sites can lead to penalties.
100. Outbound link quality
Linking to credible sources, especially those with high authority like .edu or .gov TLDs, can improve Google’s understanding of your page's context and boost your rankings. A study found a correlation between outbound link quality and rankings.
101. Outbound Link Quantity
Outbound links can enhance your page’s ranking as long as they are not excessive. Excessive linking to spammy sites can lead to penalties.
102. Number of Outbound Links Per Page
Too many external links can diminish the PageRank passed to your page. To optimize PageRank, avoid adding too many outbound links to a single page.
103. Outbound Link Motif
The overall theme of your page can be influenced by the links you use. For example, linking to a movie-related page on a car discussion page might cause Google to categorize your page under movies.
104. Excessive Use of NoFollow
The rel="nofollow” tag tells crawlers not to follow the links. While Google states excessive use of this tag isn’t a ranking factor, many SEOs avoid overusing it.
105. Internal page link quality
When you link internally, higher-authority pages may pass more equity to your newer pages than if you link lots of new pages together.
106. Internal Page Link Quantity
[pic]The number of internal links to a page can show its relevance to other information on your site. However, too many internal links can cause problems.
107. Internal Link Anchor Text
Anchor text for internal links can help contextualize them for users and crawlers. Updating internal link anchor text to be more understandable can improve context detection.
108. Broken or 404 Links
Excessive broken links can signal a poor user experience to Google and result in demotion. Regularly audit your site to fix broken links.
109. Excessive 301 Redirects
Using too many 301 redirects can cause Google to stop crawling your page and diminish PageRank.
110. Cloaking
Cloaking, where a page is listed under one context and redirects users to another, can lead to severe penalties, including de-indexing.
111. Affiliate Links
Excessive linking to affiliate sites can result in penalties. While affiliate sites can rank successfully, Google scrutinizes sites that earn revenue from affiliate programs.
112. Widget Links
Unnatural linking from widgets can result in penalties. Use the rel="nofollow” tag for widget links to avoid this issue.
113. Hidden Affiliate Links
Hiding affiliate links, especially through cloaking, will result in penalties from Google.
114. Links to Bad Neighborhoods
Linking to disreputable sources can lead to penalties for spam.
115. Selling Links
Selling links without using the rel="nofollow” tag and disclosing the sponsored nature of the link can result in demotion. Google requires transparency for paid links.
Optimizing these factors can significantly improve your site’s visibility and performance in search results.
SEO Ranking Factors: Inbound Links
Inbound links, also known as backlinks, are crucial for successful SEO. Links from reputable websites signal to Google that your site is trusted, helping your pages and overall site rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs). This concept has been integral to Google's ranking algorithm since the 1990s, and it remains important today.
116. Quantity of Linking Root Domains
The number of unique websites linking to you is one of the most significant ranking factors. A study of one million search results found this factor correlates with higher rankings more than any other.
117. Age of Linking Domain
Older domains linking to you are generally more trusted and perform better than newer ones.
118. Authority of Linking Domain
Google values links from authoritative domains more highly, as they are considered more trustworthy.
119. Authority of Linking Page
The authority of the specific page linking to you also impacts your ranking.
120. Sudden Influx of Links
A sudden spike in the number of links may indicate paid or traded links, which can lead to penalties. This tactic is also used in negative SEO attacks by competitors.
121. Quantity of Links from Individual C-Class IPs
Unique C-class IP addresses indicate diverse sources of backlinks, which is positive for SEO. However, black-hat SEOs often try to exploit this factor.
122. Quantity of Links from Same C-Class IPs
A large number of links from the same C-class IP address may signal link schemes, resulting in penalties.
123. Quantity of Total Linking Pages
The total number of pages linking to yours plays a significant role in your ranking.
124. Links from Certain TLDs
While Google denies different TLDs have varying link power, links from .gov and .edu sites appear to carry more weight.
125. Links from Competitors
Links from competitors’ sites can have a greater impact on your ranking than links from non-competitors.
126. Links from Bad Neighborhoods
Links from disreputable sites can harm your domain’s reputation. Use Google’s disavow tool to remove such links, but only if you have a penalty or purchased links.
127. Links from Low-Quality Directories
Backlinks from low-quality directories are considered unnatural links by Google and can hurt your SEO strategy.
128. Links from Unrelated Sites
A high number of links from unrelated sites increases the risk of a manual penalty from Google.
129. Links from Articles or Press Releases
Excessive links from press releases or articles are now seen as link schemes due to past abuse.
130. Co-Citations
Co-citations occur when two websites mention each other without linking, indicating a content-driven connection. This concept relates to co-occurrence, which involves the frequency and proximity of keywords on a website and their relationship with one another, tying into LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing).
131. Unlinked Brand Mentions
Some SEOs believe that Google recognizes unlinked brand mentions. While not considered links, these mentions can have indirect effects by prompting users to search for your brand later.
132. High Link Percentage from Low-Quality Sites
Receiving many links from low-quality sites, such as spammy blogs and forum profiles, can lead to penalties. This suggests your website is associated with black-hat SEO practices.
133. Links from Diverse Sources
Links from a variety of sources carry more weight than links from a single source, indicating a well-rounded link profile.
134. Links from Relevant Sources
Links from domains in a similar niche are more beneficial than those from unrelated sites, helping your site rank better.
135. Linking Domain Relevancy
Google penalizes sites with numerous links from irrelevant domains, as this indicates link schemes.
136. Links from Sites on Relevant Page Levels
According to the Hilltop algorithm, links from "expert" pages can boost your site's authority and ranking.
137. Links from Authority Sites
Multiple links from authority pages enhance your ranking, based on the Hilltop algorithm.
138. Links from Wikipedia
Although Wikipedia uses nofollow links, brand mentions may still impact your site’s ability to rank. Tools like WikiGrabber can help find relevant pages with broken links.
139. Links from Hub Pages
Creating internal link hubs for different topics can improve your page rankings. For instance, a resource hub for educational articles can help organize your site better.
140. Links from Independent Sites
Links from independent or "real” websites may be more valuable than those from blogs. Google has not confirmed this factor, but it's believed to be beneficial.
141. Links from 301 Redirects
Links from 301 redirects are similar to direct links but may pass less equity. Google states that the PageRank dissipated through a 301 is identical to that through a link.
142. Links from Forums
To combat spamming, Google may value forum links less than links from other sites.
143. Google Penguin and Link Building
The Penguin update penalizes sites using black-hat techniques to obtain links and artificially boost their SERP rankings.
144. Sitewide Links
Google counts sitewide links as a single link, though they still contribute to SERPs.
145. TrustRank of Linking Site
Links from high TrustRank sites pass more trust to you. A 2006 Google patent supports the importance of TrustRank in the algorithm.
146. Quantity of Links on Linking Page
Pages with many links pass less equity to each link. This ties into the outbound links factor.
147. Link Anchor Text

Anchor text indicates relevancy. While optimizing internal links for keywords is useful, focus on making anchor text informative and helpful for users.
148. Similar Link Text
Consistent context around links helps Google understand your page's topic better, aiding in ranking for various searches.
149. Link Titles

Link titles, which appear when users hover over a link, provide additional context for Google crawlers.
150. Link Location
Links within the main content are more valuable than those in sidebars or footers. Google treats footer links differently as they may lack editorial weight.
151. Link Location in Body Copy
Links placed higher in the body copy are considered more important by Google crawlers.
152. Country-Specific TLDs
Links from country-specific domains can improve rankings in those countries.
153. NoFollow Links
Google generally doesn’t follow nofollow links, meaning they don't pass link equity. However, some SEOs believe Google may occasionally follow them.
154. Link Velocity
Positive link velocity, where you gain more links than you lose, helps in SERPs. Negative link velocity can harm your rankings.
155. Natural Link Profile
Sites with a natural link profile rank higher than those appearing to buy links.
156. Reciprocal Links
Excessive reciprocal links can reduce your rankings. Google considers them part of a link scheme.
157. Temporary Link Schemes
Google can detect and penalize sites involved in short-lived link schemes.
158. User-Generated Content Links
Google distinguishes between site owner and user-generated content links. Manipulating this can lead to penalties for user-generated spam.
159. Word Count of Page
Longer pages with links are more credible. For instance, a link from a 1800-word page is more valuable than one from a 100-word page. Google somewhat disputes this factor, stating word count isn't necessarily indicative of quality.
160. Quality of Page Content
High-quality sources linking to you enhance your credibility and ranking.
161. Link Age
Older links carry more weight than newer ones. A Google patent suggests this factor serves as a trust signal.
162. TrustRank
Proximity to high-authority sites in terms of links increases your TrustRank and ranking. TrustRank measures various trust signals used by Google.
163. Guest Blog Posts
Guest blogs can help your site if not overused. Avoid turning guest blogging into a link scheme to prevent penalties.
SEO Ranking Factors: User
As a site owner, some SEO ranking factors are beyond your control because search engines like Google prioritize individual users. They request volunteer feedback and employ usability specialists to enhance user experience. Your site, despite your efforts, may not appear in search results depending on specific user data. Users not logged into Google properties may see one SERP, while those who are logged in may see a customized SERP based on their browsing history, favorite sites, and more. These factors make SEO challenging.
164. Query Timeliness
Google prioritizes timely results, sometimes even showing tweets for time-sensitive queries like news. This can push your listing further down the SERP, reducing its visibility.
165. SERP Diversity
Google aims to display diverse, high-quality results rather than multiple pages from the same domain. A recent update limits the number of times a single domain can appear in SERPs to ensure variety.
166. User Browsing History
If a user is signed into Google while browsing, Google records their historical data and preferences. For example, if a user frequently visits Site A, Google is likely to rank that site higher for that user’s searches.
167. User Search History
Google tracks users' queries as a personalization measure, influencing the results they see. For example, if you search for "televisions" and then "reviews," Google may prioritize sites with television reviews.
168. Brand Search
When a user searches for a specific brand, Google prioritizes results for that brand, even if you rank for similar keywords. This helps Google recognize your brand as real and genuine.
169. Pogo-Sticking
Pogo-sticking occurs when users click on a search result and immediately return to the SERP. Although Google claims it tries "not to use signals like that when it comes to search," many SEOs consider pogo-sticking a ranking factor.
SEO Ranking Factors: Google Algorithm
In the realm of SEO, you're often operating within Google's ecosystem. Google can introduce updates and algorithm changes at any time, including temporary ones that briefly impact SERPs. Here are some features and factors Google uses in its algorithm and on its SERPs that can influence a page’s ability to rank.
170. "Google Dance"
"Google Dance" refers to sudden, short-term changes in SERP rankings. SEOs suspect that Google shuffles ranking criteria to detect domains using black-hat strategies, based on a 2012 Google patent.
171. Google Webmaster Tools Warning
Google notifies site owners about unnatural links. Typically, the site’s rank will drop until the issue is resolved.
172. Google Sandbox
New sites with an unnatural surge in links might be placed in Google's sandbox, limiting their visibility on SERPs, even if they seem popular.
173. Disavow Tool
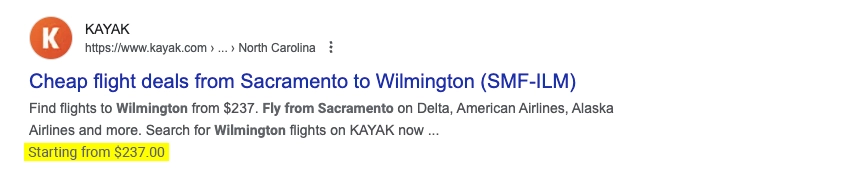
Webmasters can use the Disavow Tool to mitigate the impact of negative SEO factors, like unnatural links. Google advises using this tool only if you have a penalty and an influx of spammy links. Misuse can harm your SEO performance.
174. Transactional Searches
Google adjusts SERPs based on perceived user intent, especially for transactional queries. For example, travel-related searches may show departure times and pricing in the SERPs.
175. Shopping Results
Google Shopping results can appear in organic SERPs for transactional queries, pushing down other listings. Websites using Google Shopping Campaigns can leverage this factor.
176. Image Results
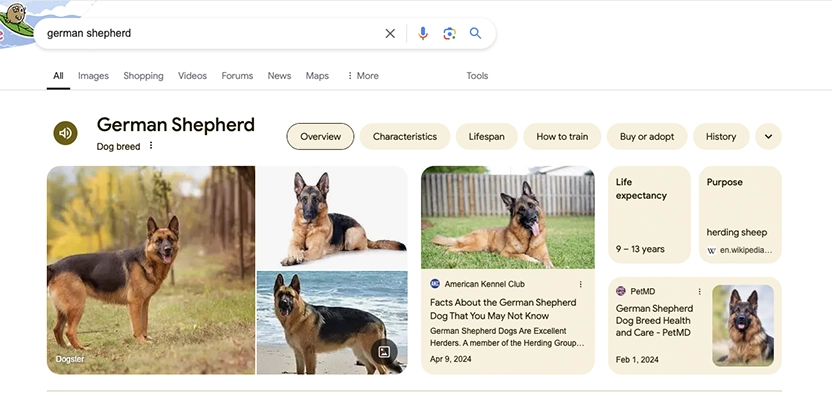
Google sometimes displays image strips for common queries, which can push down organic rankings. Optimizing your images for search can help take advantage of this factor.
177. Single-Site Results
Queries heavily favoring a specific domain might result in SERPs listing only that site, excluding others even in related fields.
178. SafeSearch
Google’s SafeSearch feature filters out adult or profane material from search results.
179. Big Brand Preference
Larger, well-known brands may receive preferential treatment due to their established reputations. Google states that this affects a small number of queries, aiming to return the best results for users.
180. Brand Mentions in the News
Brand mentions in news articles can receive preferential treatment in SERPs.
181. Brand + Keyword Search
When users search using a brand name plus a keyword (e.g., "apple iphone price"), the brand’s website (if it’s Apple) may receive a ranking boost.
182. Google News Box
News-related queries or those with many relevant new pages activate the Google News Box, giving priority to recent updates.
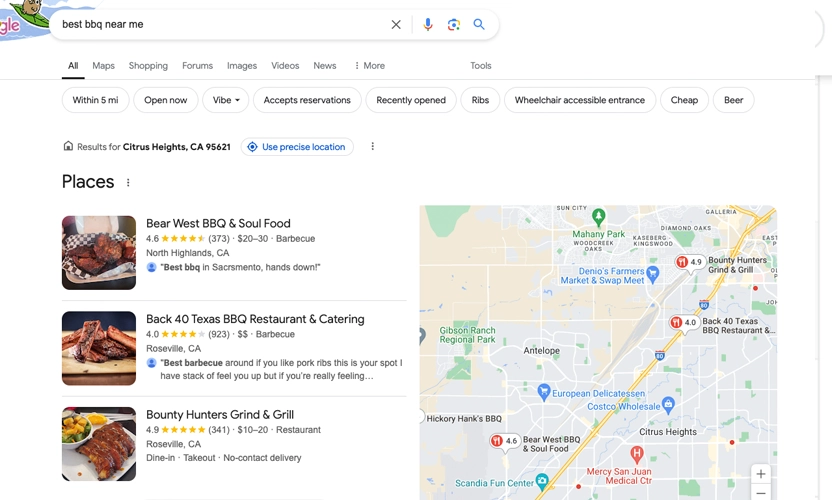
183. Local Searches
Businesses with Google My Business listings in a user’s area will appear above non-local competitors. Local searches can also change the SERP format, benefiting locally optimized businesses.
184. Country or Geo-Targeting
Google prefers sites with country-specific IP addresses matching the user’s location.
185. Domain Diversity
The Bigfoot update reduced the number of unique domains in favor of relevancy. The recent diversity update further limits the number of times a domain can appear in SERPs.
186. Easter Egg Results
Google’s Easter eggs may temporarily alter SERPs based on gags or fun additions, though they typically last for a limited time.
187. Google Chrome Bookmarks
Frequently bookmarked pages in Google Chrome might receive a boost in SERPs, as Google collects data from Chrome users.
188. Google Toolbar Data
Google collects data from its browser toolbars and incorporates it into SERPs, though specifics remain unconfirmed.
189. Human Editors
Google’s patent from 2000 allows for human editors to manually edit search results. While unlikely to directly impact your site, their findings could influence future algorithm updates.
190. Manual Penalties
Google continues to issue manual penalties, which can significantly impact your rankings. Adhering to white-hat SEO practices is crucial to avoid penalties.
191. Reconsideration Requests
After making necessary changes, filing a reconsideration request allows Google to re-examine your site and potentially remove a penalty, aiding in your site's recovery.
SEO Ranking Factors: Social
Social media's role in search engine ranking factors is somewhat ambiguous, especially for search engines like Google. However, search engines like Bing openly acknowledge using social media as an SEO ranking factor. Although its impact is minimal, it's essential to understand how social media can influence your rankings.
192. Social Sharing Sites
Links from platforms like Reddit and Digg are often nofollow, but some high-ranking links do get followed, potentially impacting SEO.
193. Social Media Verification
[pic]Verifying your social media accounts builds trust with your followers and may positively influence your rankings. Google filed a patent in 2013 for detecting fake online social media accounts, indicating its interest in verified accounts.
194. Social Shares
[pic]While social shares are not a ranking factor for Google, they are for Bing. There is a correlation between social shares and rankings in Google search results, even if it's indirect.
195. Twitter Account
Bing uses Twitter as a ranking factor, considering the authority of users and the links they share. Google no longer uses Twitter in the same way.
196. Twitter Account Authority
[pic]Bing evaluates the social authority of Twitter users, considering factors like follower count, which can add weight to search listings.
197. Number of Tweets
[pic]Bing assesses the popularity, usefulness, and relevancy of shared links by looking at the number of tweets. High sharing by genuine users can help improve rankings on Bing.
198. Facebook Account
Bing checks links shared on Facebook, including those from personal, public user, and business pages.
199. Facebook Account Authority
While Bing does not assess the authority of Facebook users, it uses Twitter to gauge the quality of Facebook shares and links.
200. Number of Facebook Shares
[pic]Bing determines the popularity and relevancy of links by examining the number of Facebook shares. High sharing can indicate relevance and impact search results.
201. Pinterest Boards
Bing includes Pinterest boards in its image search results, particularly from users with significant followings, indicating the boards' popularity and relevance.
Hear about the latest and most important SEO ranking factors
As search engines like Google and Bing continuously update their algorithms, staying up-to-date can be challenging for businesses, marketers, and SEOs. However, our Revenue Weekly newsletter can help you stay informed about the latest and most important SEO ranking factors.
Subscribe today to start receiving actionable tips, updates, and more directly in your inbox!